Most of these issues can be caused from sensor faults or terminal contact issues with high resistance.
P0390-CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR CIRCUIT - BANK 2 SENSOR 2
NOTE: The CMP Sensor is a dual read sensor reading both camshafts of it's correlating bank.
View attachment 204403
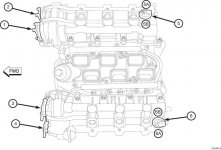
3.2L/3.6L VVT Component Locations
CALLOUT DESCRIPTION
1 VVT Actuator Bank 1 Position 1 (Intake)
2 VVT Actuator Bank 1 Position 2 (Exhaust)
3 VVT Actuator Bank 2 Position 1 (Intake)
4 VVT Actuator Bank 2 Position 2 (Exhaust)
5 Bank 1 Camshaft Sensor
5A CMP Bank 1 Sensor 1 (Exhaust)
5B CMP Bank 1 Sensor 2 (Intake)
6 Bank 2 Camshaft Sensor
6A CMP Bank 2 Sensor 1 (Exhaust)
6B CMP Bank 2 Sensor 2 (Intake)
Variable Valve Timing (VVT) allows the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to monitor and adjust the position of each Camshaft, based on desired torque levels and engine operating conditions. The PCM controls solenoid operated control valves located on the front of the engine. There is one solenoid for each Camshaft, used to direct oil pressure to hydraulic actuators mounted between each Camshaft and its driving sprocket. The oil pressure alters the angular position or phasing of each Camshaft relative to Crankshaft rotation. A sensor is used to monitor the position of each Camshaft. There are four separate Camshafts that the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) requires positional information from. There are two Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensors with each CMP Sensor consisting of four circuits. The sensors are located at the top rear of each valve cover. On the end of each Camshaft is a magnetic encoder that is programmed with a magnetic pattern. The PCM provides a 5-Volt supply and a sensor ground circuit to the CMP Sensor and the CMP Sensor provides two Camshaft positional signals, the intake and exhaust camshaft position, to the PCM. The sensor detects the magnetically encoded information, a series of magnetic peaks and valleys, from the encoder. As each Camshaft rotates, the magnetic encoded pattern passes by the CMP Sensor creating a changing magnetic field at the sensor face. The changing magnetic field is interpreted by the sensor electronics and a digital output, ON/OFF or HIGH/LOW pattern, is produced. The length of the pulse width generated by the CMP varies in size based on the velocity of the Camshaft. The PCM decodes the digital pattern to identify the Camshaft position. The information from each individual Camshaft along with the Crankshaft information is used to control and sequence the Variable Valve Timing (VVT) system and fuel injection events.
When Monitored: During engine cranking and with the engine running. Battery voltage greater than 10.0 volts. Set Condition: At least five seconds or 2.5 engine revolutions have elapsed with Crankshaft Position Sensor signals present but no camshaft position sensor signal. One Trip Fault. Three good trips to turn off the MIL. If the vehicle is equipped with the stop/start feature, the system will be disabled when this DTC is active.
Possible Causes
(F856) 5-VOLT SUPPLY CIRCUIT SHORTED TO VOLTAGE
(F856) 5-VOLT SUPPLY CIRCUIT OPEN
(F856) 5-VOLT SUPPLY CIRCUIT SHORTED TO GROUND
(K445) CMP SENSOR SIGNAL 2/2 CIRCUIT SHORTED TO VOLTAGE
(K445) CMP SENSOR SIGNAL 2/2 CIRCUIT OPEN
(K445) CMP SENSOR SIGNAL 2/2 CIRCUIT SHORTED GROUND
(K445) CMP SENSOR SIGNAL 2/2 CIRCUIT SHORTED TO THE (F856) 5-VOLT SUPPLY CIRCUIT
(K900) SENSOR GROUND CIRCUIT OPEN
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR 2
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
Always perform the Pre-Diagnostic Troubleshooting procedure before proceeding. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
Diagnostic Test
1.ACTIVE DTC
NOTE: Diagnose and repair any 5–Volt Reference DTCs that are present before continuing with this test procedure.
NOTE: Diagnose and repair any Dual Stage Oil Pump or Oil Pressure related DTCs that are present before continuing with this test procedure.
NOTE: Diagnose & Repair any VVT related issues or faults before continuing with this test procedure. Anything that affects the engines VVT system may cause a CMP Sensor DTC to set. Verify that there are no engine mechanical issues that may be causing the fault to set such as but not limited to the timing chain, camshafts and sprockets, camshaft phasers, oil quality, level or oil pressure issues.
1. Turn the ignition on.
2. With the scan tool, read DTCs. Copy DTC and Freeze Frame information.
3. Start the engine and allow it to idle or crank the engine if it will not start. Attempt to operate vehicle under conditions similar to freeze frame data
WARNING: When the engine is operating, do not stand in direct line with the fan. Do not put your hands near the pulleys, belts or fan. Do not wear loose clothing. Failure to follow these instructions may result in possible serious or fatal injury.
4. With the scan tool, read the active DTCs.
Is the DTC Active at this time?
Yes
Go To 2
No
Go To 11
2.OTHER CAM SENSOR DTCS ACTIVE
Is the P0345 or P0349 DTC also active at this time?
Yes
Go To 3
No
Go To 6
3.CHECK THE (F856) 5-VOLT SUPPLY CIRCUIT
1. Turn the ignition off.
2. Disconnect the CMP Sensor harness connector.
3. Ignition on, engine not running.
4. Measure the voltage on the (F856) 5-Volt Supply circuit in the CMP Sensor harness connector.
Is the voltage between 4.8 and 5.2 volts?
Yes
Go To 4
No
Repair the (F856) 5–Volt Supply circuit for an open or high resistance. Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
4.CHECK THE (K900) SENSOR GROUND CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN OR HIGH RESISTANCE
1. Turn the ignition off.
2. Disconnect the PCM C2 harness connector.
CAUTION: Do not probe the PCM harness connectors. Probing the PCM harness connectors will damage the PCM terminals resulting in poor terminal to pin connection. Install the GPEC Diagnostic Adaptor to perform the diagnosis.
3. Connect the Adapter, GPEC Diagnostic
.
4. Measure the resistance of the (K900) Sensor ground circuit from the CMP Sensor harness connector to the GPEC Adaptor.
Is the resistance below 5.0 Ohms?
Yes
Go To 5
No
Repair the (K900) Sensor ground circuit for an open or high resistance. Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
5.CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
1. Remove and exchange the CMP Sensor with the CMP Sensor on the opposite bank.
NOTE: Inspect the Camshaft magnetic target for damage in accordance with the service information. If a problem is found repair as necessary.
2. Reconnect the PCM C2 and Cam Sensor harness connectors.
3. Turn the ignition on,
4. With the scan tool, erase DTCs.
5. Start the engine and allow it to idle or crank the engine if it will not start. Attempt to operate vehicle under conditions similar to freeze frame data
6. With the scan tool, read DTCs.
Did the CMP Sensor DTCs for the opposite bank set as active?
Yes
Replace the Camshaft Position Sensor in accordance with the service information. (Refer to 08 - Electrical/8I - Ignition Control/SENSOR, Camshaft Position - Removal). Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
No
Go To 10
6.CHECK THE (K445) CMP SENSOR SIGNAL 2/2 CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO VOLTAGE
1. Disconnect the CMP Sensor harness connector.
2. Measure the voltage on the (K445) CMP Sensor Signal 2/2 circuit in the CMP Sensor harness connector.
Is the voltage above 5.2 volts?
Yes
Repair the (K445) CMP Sensor Signal 2/2 circuit for a short to voltage. Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
No
Go To 7
7.CHECK THE (K445) CMP SENSOR SIGNAL 2/2 CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO GROUND
1. Turn the ignition off.
2. Disconnect the PCM C2 harness connector.
3. Measure the resistance between ground and the (K445) CMP Sensor Signal 2/2 circuit at the CMP Sensor harness connector.
Is the resistance above 10k Ohms?
Yes
Go To 8
No
Repair the short to ground in the (K445) CMP Sensor Signal 2/2 circuit. Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
8.CHECK THE (K445) CMP SENSOR SIGNAL 2/2 CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN/HIGH RESISTANCE
1. Measure the resistance of the (K445) CMP Sensor Signal 2/2 circuit between the CMP Sensor harness connector and the GPEC Adaptor.
Is the resistance below 5.0 Ohms?
Yes
Go To 9
No
Repair the (K445) CMP Sensor Signal 2/2 circuit for an open or high resistance. Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
9.CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
1. Remove and exchange the CMP Sensor with the CMP Sensor on the opposite bank.
NOTE: Inspect the Camshaft sprocket for damage in accordance with the service information. If a problem is found repair as necessary.
2. Reconnect the PCM C2 and Cam Sensor harness connectors.
3. Turn the ignition on,
4. With the scan tool, erase DTCs.
5. Start the engine and allow it to idle or crank the engine if it will not start.
6. With the scan tool, read DTCs.
Did the CMP Sensor DTCs for the opposite bank set as active?
Yes
Replace the faulty Camshaft Position Sensor. (Refer to 08 - Electrical/8I - Ignition Control/SENSOR, Camshaft Position - Removal). Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
No
Go To 10
10.POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
1. Perform any Technical Service Bulletins that may apply.
2. Anything that affects the engines VVT system may cause a CMP Sensor DTC to set. Before replacing the PCM, verify that there are no engine mechanical issues that may be causing the fault to set such as but not limited to the timing chain, camshafts and sprockets, camshaft phasers, oil quality, level or oil pressure issues.
3. Using the wiring diagram/schematic as a guide, inspect the wiring and connectors between the related Sensor and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
4. Look for any chafed, pierced, pinched or partially broken wires.
5. Look for broken, bent, pushed out or corroded terminals. Verify that there is good pin to terminal contact in the related Sensor and the Powertrain Control Module connectors.
Were there any issues?
Yes
Repair as necessary. Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
No
Replace and program the Powertrain Control Module in accordance with the service information. (Refer to 08 - Electrical/8E - Electronic Control Modules/MODULE, Powertrain Control - Removal). Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
11.WIRE HARNESS/CKP SENSOR INSPECTION
1. Turn the ignition off.
2. Disconnect the harness connectors at the PCM and Cam Sensor and inspect for wire chaffing or rub conditions, terminals pushed out on the wiring connector, bent terminals at the PCM and Crank Sensor, water in the connector cavities, presence of corrosion on the terminals of the connectors or components.
3. Visually inspect the mounting area of Cam Sensor for debris/damage or a loose sensor. Remove the Cam Sensor and inspect the end of the sensor for signs of damage or debris. Rotate the engine and if possible, inspect the target wheel for any signs of damage. Reinstall the Cam Sensor and ensure that the sensor is properly installed and torqued to proper specification.
NOTE: Due to the fact that this DTC is set by an intermittent loss of the signal, the most likely cause is a poor connection at the Cam Sensor or PCM terminals, or a poor signal between the Cam Sensor and target wheel. Because of this, unplugging and reconnecting the harness connectors, or repositioning the Cam Sensor will often repair the condition that set the DTC.
Were any problems found?
Yes
Perform the appropriate repair. Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
No
Go To 12
12.CHECK THE VEHICLE’S REPAIR HISTORY
1. Check the history of the vehicle for previous Cam Sensor related DTCs within the past 90 days.
Did the repair history show that the vehicle was in dealership for a Cam Sensor fault within the past 90 days?
Yes
Replace the Cam Sensor in accordance with the service information. Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).
No
Test complete. Reconnect the harness connectors, and erase the DTC. The most likely cause was a poor connection at one of the harness connectors. Verify the DTC does not return. Perform the POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 28 - DTC-Based Diagnostics/MODULE, Powertrain Control (PCM) - Standard Procedure).